Sand Fleas on Humans: A Detailed Look
Have you ever wondered what it feels like to be bitten by a sand flea? These tiny creatures, often overlooked, can cause quite a stir when they decide to make a meal out of your skin. In this article, we will delve into the world of sand fleas, exploring their characteristics, behavior, and the impact they can have on humans.
What are Sand Fleas?
Sand fleas, also known as chiggers or no-see-ums, are tiny arachnids that belong to the family Trombiculidae. They are found in sandy environments, particularly in coastal areas, deserts, and grasslands. Despite their small size, they can be quite pesky and cause discomfort to humans and animals alike.
Appearance and Size
Sand fleas are typically less than 1 millimeter in length, making them almost invisible to the naked eye. They have a flat, oval-shaped body and are usually tan or brown in color. Their legs are long and slender, allowing them to move quickly through the sand.
Behavior and Diet
Sand fleas are parasitic creatures that feed on the blood of their hosts. They have specialized mouthparts that allow them to pierce the skin and suck blood. Once they find a suitable host, they will attach themselves and feed for several days before dropping off to digest their meal.
These tiny creatures are most active during the warmest parts of the day, typically in the late afternoon and early evening. They are attracted to hosts through carbon dioxide and body heat, making them more likely to bite humans during outdoor activities in sandy areas.
The Biting Process
When a sand flea bites, it injects its saliva into the skin, which contains enzymes that break down the host’s blood. This saliva can cause an allergic reaction in some individuals, leading to itching, redness, and swelling at the bite site.
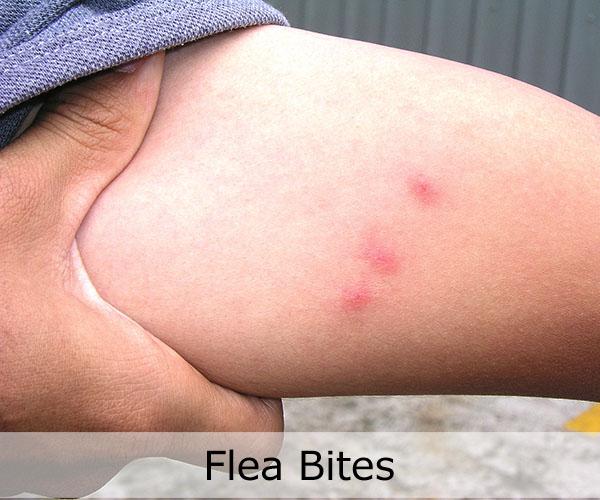
After feeding, the sand flea will drop off and leave behind a small, red bump on the skin. This bump can be itchy and may last for several days. In some cases, the bite can become infected if it is scratched or if the host has a weakened immune system.
Preventing Sand Flea Bites
Preventing sand flea bites is crucial, especially if you plan to spend time in sandy environments. Here are some tips to help you avoid these pesky creatures:
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and pants when possible.
- Apply insect repellent containing DEET or picaridin to exposed skin and clothing.
- Stay in the middle of the trail or path when walking in sandy areas.
- Check your clothing and body for sand fleas after spending time in sandy environments.
Dealing with Sand Flea Bites
If you do get bitten by a sand flea, there are several ways to alleviate the discomfort:
- Wash the bite area with soap and water to prevent infection.
- Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling and itching.
- Use over-the-counter antihistamines or hydrocortisone cream to relieve itching.
- Seek medical attention if the bite becomes infected or if you experience severe allergic reactions.
Table: Sand Flea Bite Symptoms
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Itching | One of the most common symptoms, usually felt within a few hours of the bite. |
| Redness | The bite area may become red and inflamed. |
| Swelling | The bite area may swell, especially if an allergic reaction occurs. |
| Bump | A small, red bump may form at the bite site. |
| Infection | In rare cases, the bite can become infected, leading to more severe symptoms. |
Conclusion
Sand fleas may be tiny, but their bites can cause








