Saturated Sand Density: A Comprehensive Guide
Saturated sand density is a crucial parameter in various engineering and scientific fields, particularly in civil engineering, geotechnical engineering, and environmental studies. It refers to the density of sand when it is fully saturated with water. Understanding this concept is essential for assessing the behavior of soil and sand under different conditions. In this article, we will delve into the details of saturated sand density, its significance, and its measurement methods.
What is Saturated Sand Density?
Saturated sand density is the mass of saturated sand per unit volume. It is typically expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm鲁) or kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m鲁). When sand is saturated, it means that all the voids between the sand particles are filled with water. This condition is often encountered in natural environments, such as riverbeds, beaches, and construction sites.
The saturated sand density is influenced by several factors, including the grain size, shape, and sorting of the sand particles, as well as the water content. Generally, finer-grained sands have higher saturated densities compared to coarse-grained sands. Additionally, well-sorted sands tend to have higher saturated densities than poorly sorted sands.
Significance of Saturated Sand Density
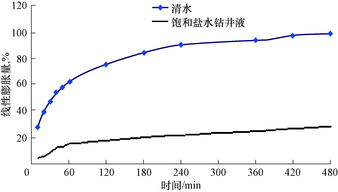
The saturated sand density plays a vital role in various engineering and scientific applications. Here are some of the key reasons why it is important:
-
Foundation Design: In civil engineering, the saturated sand density is crucial for determining the bearing capacity of foundations. It helps engineers assess whether the foundation will be stable and capable of supporting the intended load.
-
Geotechnical Engineering: In geotechnical engineering, the saturated sand density is used to evaluate the soil’s strength and stability. It helps engineers predict the behavior of soil under different loading conditions.
-
Environmental Studies: In environmental studies, the saturated sand density is important for assessing the permeability of soil and the potential for groundwater contamination.
-
Construction Projects: In construction projects, the saturated sand density is used to determine the soil’s compaction requirements and to ensure that the soil is suitable for the intended use.
Measurement of Saturated Sand Density
There are several methods to measure the saturated sand density, each with its advantages and limitations. Here are some commonly used methods:
Hydrometer Method
The hydrometer method is one of the most popular techniques for measuring the saturated sand density. It involves the following steps:
-
Prepare a suspension of the sand sample in water.
-
Allow the suspension to settle for a specific period.
-
Measure the sedimentation rate of the sand particles using a hydrometer.
-
Calculate the saturated sand density based on the sedimentation rate and the known properties of the sand sample.
Core Sampling Method
The core sampling method involves extracting a soil sample from the ground and measuring its saturated sand density. This method is particularly useful for assessing the in-situ properties of the soil. The steps involved are:
-
Excavate a soil core from the ground.
-
Wash the core to remove any loose particles.
-
Measure the weight and volume of the core.
-
Calculate the saturated sand density based on the weight and volume of the core.
Table: Comparison of Saturated Sand Density Measurement Methods
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrometer Method | Simple, cost-effective, and widely available. | Not suitable for coarse-grained sands, and requires time for settling. |
| Core Sampling Method | Accurate and provides in-situ properties. | Expensive, time-consuming, and requires specialized equipment. |
In conclusion, saturated sand density is a critical parameter in various engineering and scientific fields. Understanding its significance and measurement methods can help








