Sand Equivalent Calculation: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the sand equivalent calculation is crucial in various engineering and construction fields. It helps in determining the plasticity and compaction characteristics of soil, which are essential for the stability and durability of structures. In this article, we will delve into the details of sand equivalent calculation, its significance, and its applications.
What is Sand Equivalent?

The sand equivalent (SE) is a measure of the fines content in a soil sample. It is defined as the percentage of the soil particles that pass through a 0.075 mm sieve and are finer than the 0.075 mm sieve. The sand equivalent value is used to assess the plasticity and compaction characteristics of soil, which are critical for the design and construction of foundations, roads, and other civil engineering projects.
How to Calculate Sand Equivalent
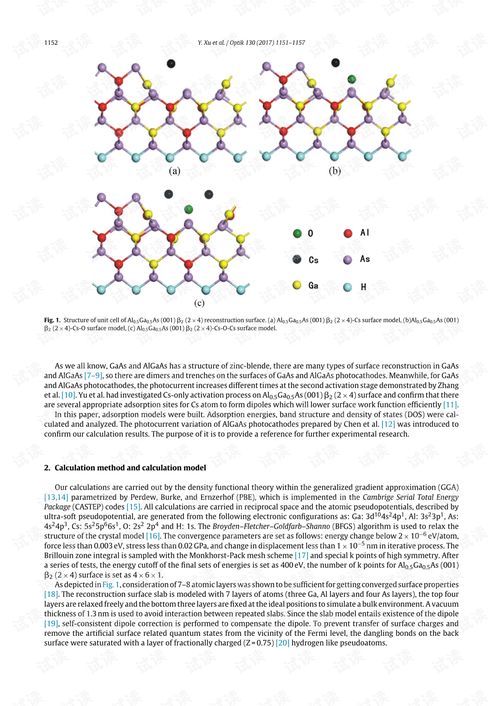
Calculating the sand equivalent involves several steps. Here’s a detailed guide:
-
Obtain a soil sample with a known weight (W1) and volume (V1).
-
Wash the soil sample with water to remove any fines that are not bound to the soil particles.
-
Filter the washed soil sample through a 0.075 mm sieve to separate the fines from the coarse particles.
-
Obtain the weight of the soil sample after washing (W2) and the weight of the soil sample after filtering (W3).
-
Calculate the weight of the fines (Wfines) by subtracting W3 from W2.
-
Calculate the weight of the coarse particles (Wcoarse) by subtracting Wfines from W1.
-
Calculate the volume of the fines (Vfines) by subtracting V3 from V1.
-
Calculate the sand equivalent (SE) using the following formula:
SE = (Wfines / Wcoarse) 100
Significance of Sand Equivalent

The sand equivalent value is significant for several reasons:
-
It helps in determining the plasticity and compaction characteristics of soil.
-
It is used to assess the suitability of soil for construction purposes.
-
It helps in designing foundations and other structures to ensure their stability and durability.
-
It is used in the construction of roads, embankments, and other civil engineering projects.
Applications of Sand Equivalent
The sand equivalent value is widely used in various engineering and construction fields. Some of the common applications include:
-
Foundation design: The sand equivalent value helps in determining the type of foundation required for a particular soil condition.
-
Compaction control: It helps in ensuring that the soil is adequately compacted during construction.
-
Soil stabilization: The sand equivalent value is used to assess the effectiveness of soil stabilization techniques.
-
Construction of roads and embankments: It helps in determining the suitability of soil for road construction and embankment design.
Table: Sand Equivalent Calculation Example
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Weight of soil sample (W1) | 100 g |
| Volume of soil sample (V1) | 50 cm鲁 |
| Weight of soil sample after washing (W2) | 90 g |
| Weight of soil sample after filtering (W3) | 80 g |
| Volume of soil sample after filtering (V3) | 40 cm鲁 |
| Sand equivalent (SE) | 100 |














