Captions for Sand: A Detailed Multidimensional Introduction
Have you ever wondered about the intricate details that make up the vast expanse of sand? Sand, often overlooked, is a fascinating and diverse material that plays a crucial role in various aspects of our lives. In this article, we will delve into the different dimensions of sand, exploring its composition, formation, uses, and environmental impact.
Composition of Sand
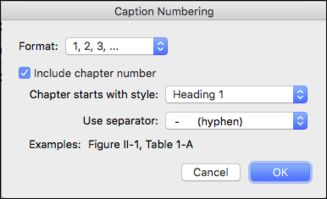
Sand is primarily composed of tiny grains of rock, minerals, and organic matter. These grains are typically less than 2 millimeters in diameter and can vary in color, shape, and texture. The most common minerals found in sand are quartz, feldspar, and mica. Quartz, in particular, is the most abundant mineral in sand, accounting for about 25% of the Earth’s crust.
Here’s a breakdown of the composition of sand:
| Mineral | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Quartz | 25% |
| Feldspar | 20% |
| Mica | 15% |
| Other minerals | 40% |
Formation of Sand
Sand is formed through a process called weathering and erosion. Over time, rocks are broken down into smaller particles by physical, chemical, and biological processes. These particles are then transported by wind, water, or ice to different locations, where they accumulate and form sand deposits. The process of sand formation can take thousands to millions of years, depending on various factors such as climate, topography, and the type of rock being weathered.
Here are some key factors that contribute to the formation of sand:
-
Physical weathering: This involves the physical breakdown of rocks into smaller particles due to factors such as temperature changes, freeze-thaw cycles, and abrasion.
-
Chemical weathering: This involves the chemical alteration of rocks, leading to the formation of new minerals and the breakdown of existing ones.
-
Biological weathering: This involves the breakdown of rocks by living organisms, such as plants, animals, and microorganisms.
-
Erosion: This involves the transportation of weathered particles by wind, water, or ice to different locations.
Uses of Sand
Sand has a wide range of uses, making it an essential material in various industries. Here are some of the most common applications of sand:
-
Construction: Sand is a key ingredient in concrete, asphalt, and mortar. It provides strength, stability, and durability to these materials.
-
Foundry: Sand is used in the foundry industry to create molds for casting metal objects. It is essential for the production of various metal products, such as car parts, machinery, and sculptures.
-
Water filtration: Sand is used in water filtration systems to remove impurities and contaminants from water, ensuring its purity and safety for drinking and other purposes.
-
Recreation: Sand is a popular material for beaches, playgrounds, and sports fields. It provides a natural and comfortable surface for various activities.
Environmental Impact of Sand Mining
While sand has numerous uses, the process of sand mining can have significant environmental impacts. Sand mining involves extracting sand from natural deposits, which can lead to several negative consequences:
-
Land degradation: Sand mining can cause the erosion of soil and the destruction of natural habitats, leading to habitat loss for various plant and animal species.
-
Water pollution: Sand mining can contaminate water sources, affecting aquatic life and human health.
-
Displacement of communities: Sand mining can displace local communities, leading to social and economic challenges.
It is crucial to implement sustainable sand mining practices and regulations to minimize these negative impacts and ensure the long-term availability of this valuable resource.
Conclusion
Sand, often













