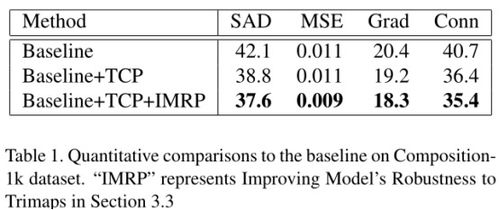
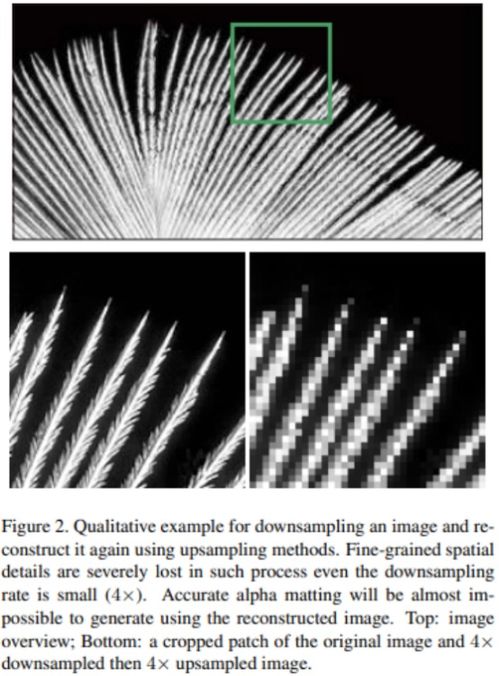
Fine Grained Sand: A Comprehensive Overview
Fine-grained sand, often referred to as fine sand, is a type of sedimentary rock that is widely used in various industries. It is characterized by its small particle size, which ranges from 0.0625 to 2 millimeters. This article will delve into the properties, applications, and production methods of fine-grained sand, providing you with a detailed understanding of this versatile material.
Properties of Fine Grained Sand
 Fine-grained sand is composed of small, rounded grains that are typically derived from the weathering and erosion of rocks. The particle size distribution of fine sand is narrow, which means that the grains are relatively uniform in size. This uniformity contributes to the material’s excellent workability and stability.
Fine-grained sand is composed of small, rounded grains that are typically derived from the weathering and erosion of rocks. The particle size distribution of fine sand is narrow, which means that the grains are relatively uniform in size. This uniformity contributes to the material’s excellent workability and stability.
One of the key properties of fine-grained sand is its high porosity. This characteristic allows the sand to absorb and retain water, making it suitable for use in construction applications where water retention is essential. Additionally, fine-grained sand has good permeability, which enables it to drain excess water effectively.
Another important property of fine-grained sand is its compressive strength. This strength is determined by the size, shape, and arrangement of the sand grains. Generally, fine-grained sand has a higher compressive strength compared to coarse-grained sand, making it more suitable for load-bearing structures.
Applications of Fine Grained Sand
 Fine-grained sand is a versatile material with a wide range of applications. Some of the most common uses of fine-grained sand include:
Fine-grained sand is a versatile material with a wide range of applications. Some of the most common uses of fine-grained sand include:
- Construction: Fine-grained sand is extensively used in the construction industry as a component of concrete, mortar, and asphalt. Its high workability and stability make it an ideal material for these applications.
- Foundry: Fine-grained sand is used in foundry operations to create molds and cores for metal casting. The sand’s ability to hold shape and resist heat makes it an excellent choice for this purpose.
- Landscaping: Fine-grained sand is often used in landscaping projects for pathways, driveways, and as a base material for paver installations. Its natural appearance and ease of maintenance make it a popular choice for outdoor applications.
- Water Treatment: Fine-grained sand is used in water treatment plants to remove impurities from water. The sand’s ability to filter out particles and absorb contaminants makes it an effective material for water purification.
Production Methods of Fine Grained Sand
 Fine-grained sand is produced through various methods, depending on the source material and desired particle size distribution. Here are some common production methods:
Fine-grained sand is produced through various methods, depending on the source material and desired particle size distribution. Here are some common production methods:
- Quarrying: Fine-grained sand is often extracted from natural sand quarries. The sand is mined using excavation equipment and then processed to achieve the desired particle size distribution.
- Washing: After mining, the sand is washed to remove impurities such as clay, silt, and organic matter. This process is typically carried out using water and screening equipment.
- Screening: Screening is used to separate the sand into different particle size fractions. Fine-grained sand is obtained by passing the sand through a series of screens with progressively smaller openings.
- Drying: In some cases, the fine-grained sand may need to be dried to reduce its moisture content. This is usually done using a drying drum or a belt dryer.
Table: Comparison of Fine Grained Sand Production Methods
| Production Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Quarrying | High production capacity, low cost | Environmental impact, high energy consumption |
| Washing | Removes impurities, improves quality | High water consumption, potential for environmental impact |
| Screening | Uniform particle size distribution | May require multiple stages, energy-intensive |
| Drying | Reduces moisture content, improves storage stability | Energy-intensive, potential for dust generation |
Conclusion
Fine-grained sand is a valuable material with numerous applications across various industries. Its unique












