Sand Silt Permeability: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the permeability of sand and silt is crucial in various fields, including civil engineering, environmental science, and geology. Permeability refers to the ability of a material, in this case, sand and silt, to allow fluids to pass through it. This guide will delve into the details of sand and silt permeability, exploring its significance, measurement methods, and applications.
What is Permeability?
Permeability is a measure of how easily a fluid can flow through a porous material. In the context of sand and silt, it determines how water or other fluids can move through these sedimentary materials. The permeability of a soil or sediment is influenced by several factors, including particle size, shape, and arrangement.
Particle Size and Shape
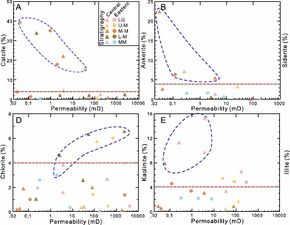
The size and shape of particles in sand and silt significantly impact their permeability. Generally, finer particles, such as silt, have lower permeability compared to coarser particles, like sand. This is because finer particles have smaller interparticle spaces, making it more difficult for fluids to pass through. Additionally, the shape of the particles can affect the flow path and resistance to fluid movement.
Table 1: Particle Size and Permeability
| Particle Size | Permeability (cm/s) |
|---|---|
| Sand | 1 – 100 |
| Silt | 0.01 – 0.1 |
Porosity and Permeability
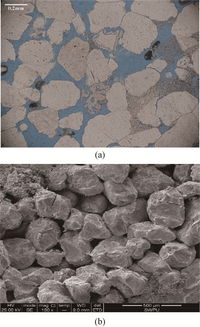
Porosity is the measure of void spaces within a material, and it is closely related to permeability. Higher porosity generally corresponds to higher permeability, as more space is available for fluid flow. However, the relationship between porosity and permeability is not always linear, as other factors, such as particle arrangement, can also influence permeability.
Measurement Methods
Several methods can be used to measure the permeability of sand and silt. The most common methods include the constant head permeameter, falling head permeameter, and the permeameter with a variable head. Each method has its advantages and limitations, and the choice of method depends on the specific requirements of the study.
Applications
The permeability of sand and silt has numerous applications across various fields. In civil engineering, it is essential for assessing the stability of foundations, designing drainage systems, and evaluating the potential for soil erosion. In environmental science, permeability is crucial for understanding groundwater flow and contaminant transport. Geologists also use permeability data to study the behavior of sedimentary rocks and the formation of oil and gas reservoirs.
Case Study: Construction of a Highway
Consider a hypothetical scenario where a highway is being constructed through a region with sandy and silty soils. The permeability of these soils is a critical factor in ensuring the stability of the highway foundation. By conducting permeability tests, engineers can determine the appropriate foundation design and drainage system to prevent soil erosion and ensure long-term stability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sand and silt permeability is a vital aspect to consider in various fields. Understanding the factors influencing permeability and the appropriate measurement methods can help engineers, scientists, and researchers make informed decisions. By considering permeability, we can ensure the stability of structures, protect the environment, and unlock the potential of natural resources.








