Understanding the Void Ratio of Sand: A Comprehensive Guide
The void ratio of sand is a crucial parameter in geotechnical engineering, construction, and soil mechanics. It refers to the ratio of the volume of voids (empty spaces) to the total volume of the soil. This article delves into the various aspects of the void ratio of sand, providing you with a detailed and multi-dimensional understanding.
What is Void Ratio?
The void ratio is defined as the volume of voids divided by the volume of solids. It is expressed as a dimensionless quantity and is typically represented by the symbol e. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
| Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|
| e | Void ratio |
| Vv | Volume of voids |
| Volume of solids |
For example, if a sample of sand has a volume of 100 cm鲁 and the volume of voids is 50 cm鲁, the void ratio would be 0.5 (50 cm鲁 / 100 cm鲁).
Significance of Void Ratio

The void ratio of sand plays a vital role in various engineering applications. Here are some of the key reasons why it is important:
-
Stability of soil: The void ratio determines the stability of soil. A higher void ratio indicates a lower degree of compaction and, consequently, a lower stability. Conversely, a lower void ratio suggests a higher degree of compaction and better stability.
-
Permeability: The void ratio affects the permeability of soil. A higher void ratio means higher permeability, allowing water and other fluids to flow more easily through the soil. In contrast, a lower void ratio results in lower permeability.
-
Shear strength: The void ratio influences the shear strength of soil. A higher void ratio generally leads to lower shear strength, making the soil more susceptible to failure. Conversely, a lower void ratio results in higher shear strength.
-
Compaction: The void ratio is essential in determining the degree of compaction required for soil. Proper compaction ensures that the soil can support the intended load without excessive settlement.
Factors Affecting Void Ratio
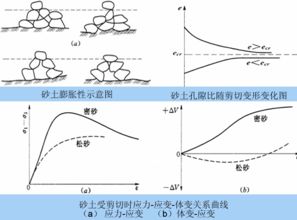
Several factors can influence the void ratio of sand. Some of the most significant factors include:
-
Water content: The water content of the soil directly affects its void ratio. As the water content increases, the void ratio also increases, and vice versa.
-
Grain size: The size of the sand particles can impact the void ratio. Generally, finer particles have a higher void ratio than coarser particles.
-
Compaction: The degree of compaction applied to the soil can alter its void ratio. Compaction reduces the void ratio by squeezing out air and water from the soil.
-
Atterberg limits: The Atterberg limits, which include the liquid limit, plastic limit, and shrinkage limit, can also influence the void ratio of sand.
Measurement of Void Ratio
There are several methods to measure the void ratio of sand. Some of the commonly used techniques include:
-
Hydrometer test: This method involves measuring the volume of soil and water in a graduated cylinder. The void ratio can then be calculated using the formula mentioned earlier.
-
Sand replacement method: In this method, a known volume of sand is added to a soil sample, and the increase in volume is measured. The void ratio can then be calculated based on the volume of sand added.
-
Core sampler: A core sampler can be used to extract a soil sample from the ground. The void ratio can then be determined by measuring the volume of voids and solids in the sample.
Applications of Void Ratio
The void ratio of sand finds applications in various fields, including:
-
Foundation design: The void ratio is crucial in












